Product Description
Product Description
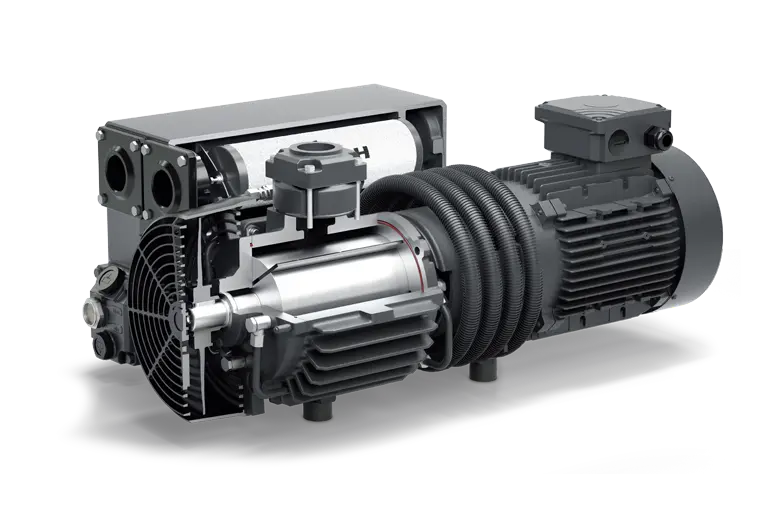
China Lab Oil Vacuum pump Two-stage rotary vane workshop Vacuum pump Mechanical pump Electric suction pump VRD series
It is mainly used in medicinal products analysis , industry of fine chemicals , biochemical pharmacy , food examination , The criminal investigation technology , etc . It is used with the precision chromatography instrument , the necessary of laboratory . This product is specially designed for laboratory , reliable and easy to use .
APPLICATION:rotary evaporator/ glass reactor / vacuum filter / distillation
Product Parameters
| MODEL | VRD-8 | VRD-16 | VRD-24 | VRD-30 | VRD-48 | VRD-65 | |
| Displacement speed m3/h (L/s) |
50Hz | 8 (2.2) | 16 (4.4) | 24 (6.6) | 30 (8.3) | 48 (13.3) | 65 (18) |
| 60Hz | 9.6 (2.6) | 19.2 (5.2) | 28.8 (7.9) | 36 (9.9) | 57.6 (16) | 78 (21.6) | |
| Ultimate partial pressure gas ballast closed (Pa) | 5x10-2 | 4x10-2 | 4x10-2 | 4x10-2 | 4x10-2 | 4x10-2 | |
| Ultimate total pressure gas ballast closed (Pa) | 5x10-1 | 4x10-1 | 4x10-1 | 4x10-1 | 4x10-1 | 4x10-1 | |
| Ultimate total pressure gas ballast open (Pa) | 3 | 8x10-1 | 8x10-1 | 8x10-1 | 8x10-1 | 8x10-1 | |
| power supply | Single/Three phase | Single/Three phase | Single/Three phase | Single/Three phase | Three phase | Three phase | |
| Power rating (kW) | 0.4/0.37 | 0.75/0.55 | 1.1/0.75 | 1.1 | 1.5 | 2.2 | |
| Intake and exhaust DN (mm) | KF16/25 | KF25 | KF25/40 | KF25/40 | KF40 | KF40 | |
| Oil capacity (L) | 0.6~1.0 | 0.9~1.5 | 1.3~2.0 | 1.3~2.0 | 3.3~4.5 | 3.3~4.5 | |
| Motor speed (rpm) | 50Hz | 1440 | 1440 | 1440 | 1440 | 1440 | 1440 |
| 60Hz | 1720 | 1720 | 1720 | 1720 | 1720 | 1720 | |
| Ambient temperature (°C) | 5 - 40 | 5 - 40 | 5 - 40 | 5 - 40 | 5 - 40 | 5 - 40 | |
| Noise level (dB) | ≤56 | ≤58 | ≤58 | ≤58 | ≤62 | ≤62 | |
| Net weight (kg) | 20 | 33 | 35 | 37 | 62 | 65 | |
Detailed Photos
1.Two-Shift adjustable gas ballast valve satisfies different requirements of condensable vapor(such as water vapor) to be exhausted out of pump in different processes.
2.Dual protection of oil anti-sucking back ensures vacuum system from oil pollution when pump stops running and needs to be easily restarted.
3.Forced oil circulation system consisted of oil pump and constant pressure oil supply mechanism ensures stable running of the pump.
4. Less components are used, easy to maintain and repair.
Company Profile
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(",").forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Oil or Not: | Oil |
|---|---|
| Structure: | Rotary Vacuum Pump |
| Exhauster Method: | Positive Displacement Pump |
| Vacuum Degree: | Low Vacuum |
| Work Function: | Maintain the Pump |
| Working Conditions: | Oil Pump |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
Can Vacuum Pumps Be Used in the Aerospace Sector?
Vacuum pumps indeed have various applications in the aerospace sector. Here's a detailed explanation:
Vacuum pumps play a crucial role in several areas of the aerospace industry, supporting various processes and systems. Some of the key applications of vacuum pumps in the aerospace sector include:
1. Space Simulation Chambers: Vacuum pumps are used in space simulation chambers to replicate the low-pressure conditions experienced in outer space. These chambers are utilized for testing and validating the performance and functionality of aerospace components and systems under simulated space conditions. Vacuum pumps create and maintain the necessary vacuum environment within these chambers, allowing engineers and scientists to evaluate the behavior and response of aerospace equipment in space-like conditions.
2. Propellant Management: In space propulsion systems, vacuum pumps are employed for propellant management. They help in the transfer, circulation, and pressurization of propellants, such as liquid rocket fuels or cryogenic fluids, in both launch vehicles and spacecraft. Vacuum pumps assist in creating the required pressure differentials for propellant flow and control, ensuring efficient and reliable operation of propulsion systems.
3. Environmental Control Systems: Vacuum pumps are utilized in the environmental control systems of aircraft and spacecraft. These systems are responsible for maintaining the desired atmospheric conditions, including temperature, humidity, and cabin pressure, to ensure the comfort, safety, and well-being of crew members and passengers. Vacuum pumps are used to regulate and control the cabin pressure, facilitating the circulation of fresh air and maintaining the desired air quality within the aircraft or spacecraft.
4. Satellite Technology: Vacuum pumps find numerous applications in satellite technology. They are used in the fabrication and testing of satellite components, such as sensors, detectors, and electronic devices. Vacuum pumps help create the necessary vacuum conditions for thin film deposition, surface treatment, and testing processes, ensuring the performance and reliability of satellite equipment. Additionally, vacuum pumps are employed in satellite propulsion systems to manage propellants and provide thrust for orbital maneuvers.
5. Avionics and Instrumentation: Vacuum pumps are involved in the production and testing of avionics and instrumentation systems used in aerospace applications. They facilitate processes such as thin film deposition, vacuum encapsulation, and vacuum drying, ensuring the integrity and functionality of electronic components and circuitry. Vacuum pumps are also utilized in vacuum leak testing, where they help create a vacuum environment to detect and locate any leaks in aerospace systems and components.
6. High Altitude Testing: Vacuum pumps are used in high altitude testing facilities to simulate the low-pressure conditions encountered at high altitudes. These testing facilities are employed for evaluating the performance and functionality of aerospace equipment, such as engines, materials, and structures, under simulated high altitude conditions. Vacuum pumps create and control the required low-pressure environment, allowing engineers and researchers to assess the behavior and response of aerospace systems in high altitude scenarios.
7. Rocket Engine Testing: Vacuum pumps are crucial in rocket engine testing facilities. They are utilized to evacuate and maintain the vacuum conditions in engine test chambers or nozzles during rocket engine testing. By creating a vacuum environment, these pumps simulate the conditions experienced by rocket engines in the vacuum of space, enabling accurate testing and evaluation of engine performance, thrust levels, and efficiency.
It's important to note that aerospace applications often require specialized vacuum pumps capable of meeting stringent requirements, such as high reliability, low outgassing, compatibility with propellants or cryogenic fluids, and resistance to extreme temperatures and pressures.
In summary, vacuum pumps are extensively used in the aerospace sector for a wide range of applications, including space simulation chambers, propellant management, environmental control systems, satellite technology, avionics and instrumentation, high altitude testing, and rocket engine testing. They contribute to the development, testing, and operation of aerospace equipment, ensuring optimal performance, reliability, and safety.

How Do Vacuum Pumps Contribute to Energy Savings?
Vacuum pumps play a significant role in energy savings in various industries and applications. Here's a detailed explanation:
Vacuum pumps contribute to energy savings through several mechanisms and efficiencies. Some of the key ways in which vacuum pumps help conserve energy are:
1. Improved Process Efficiency: Vacuum pumps are often used to remove gases and create low-pressure or vacuum conditions in industrial processes. By reducing the pressure, vacuum pumps enable the removal of unwanted gases or vapors, improving the efficiency of the process. For example, in distillation or evaporation processes, vacuum pumps help lower the boiling points of liquids, allowing them to evaporate or distill at lower temperatures. This results in energy savings as less heat is required to achieve the desired separation or concentration.
2. Reduced Energy Consumption: Vacuum pumps are designed to operate efficiently and consume less energy compared to other types of equipment that perform similar functions. Modern vacuum pump designs incorporate advanced technologies, such as variable speed drives, energy-efficient motors, and optimized control systems. These features allow vacuum pumps to adjust their operation based on demand, reducing energy consumption during periods of lower process requirements. By consuming less energy, vacuum pumps contribute to overall energy savings in industrial operations.
3. Leak Detection and Reduction: Vacuum pumps are often used in leak detection processes to identify and locate leaks in systems or equipment. By creating a vacuum or low-pressure environment, vacuum pumps can assess the integrity of a system and identify any sources of leakage. Detecting and repairing leaks promptly helps prevent energy wastage associated with the loss of pressurized fluids or gases. By addressing leaks, vacuum pumps assist in reducing energy losses and improving the overall energy efficiency of the system.
4. Energy Recovery Systems: In some applications, vacuum pumps can be integrated into energy recovery systems. For instance, in certain manufacturing processes, the exhaust gases from vacuum pumps may contain heat or have the potential for energy recovery. By utilizing heat exchangers or other heat recovery systems, the thermal energy from the exhaust gases can be captured and reused to preheat incoming fluids or provide heat to other parts of the process. This energy recovery approach further enhances the overall energy efficiency by utilizing waste heat that would otherwise be lost.
5. System Optimization and Control: Vacuum pumps are often integrated into centralized vacuum systems that serve multiple processes or equipment. These systems allow for better control, monitoring, and optimization of the vacuum generation and distribution. By centralizing the vacuum production and employing intelligent control strategies, energy consumption can be optimized based on the specific process requirements. This ensures that vacuum pumps operate at the most efficient levels, resulting in energy savings.
6. Maintenance and Service: Proper maintenance and regular servicing of vacuum pumps are essential for their optimal performance and energy efficiency. Routine maintenance includes tasks such as cleaning, lubrication, and inspection of pump components. Well-maintained pumps operate more efficiently, reducing energy consumption. Additionally, prompt repair of any faulty parts or addressing performance issues helps maintain the pump's efficiency and prevents energy waste.
In summary, vacuum pumps contribute to energy savings through improved process efficiency, reduced energy consumption, leak detection and reduction, integration with energy recovery systems, system optimization and control, as well as proper maintenance and service. By utilizing vacuum pumps efficiently and effectively, industries can minimize energy waste, optimize energy usage, and achieve significant energy savings in various applications and processes.

Are There Different Types of Vacuum Pumps Available?
Yes, there are various types of vacuum pumps available, each designed to suit specific applications and operating principles. Here's a detailed explanation:
Vacuum pumps are classified based on their operating principles, mechanisms, and the type of vacuum they can generate. Some common types of vacuum pumps include:
1. Rotary Vane Vacuum Pumps:
- Description: Rotary vane pumps are positive displacement pumps that use rotating vanes to create a vacuum. The vanes slide in and out of slots in the pump rotor, trapping and compressing gas to create suction and generate a vacuum.
- Applications: Rotary vane vacuum pumps are widely used in applications requiring moderate vacuum levels, such as laboratory vacuum systems, packaging, refrigeration, and air conditioning.
2. Diaphragm Vacuum Pumps:
- Description: Diaphragm pumps use a flexible diaphragm that moves up and down to create a vacuum. The diaphragm separates the vacuum chamber from the driving mechanism, preventing contamination and oil-free operation.
- Applications: Diaphragm vacuum pumps are commonly used in laboratories, medical equipment, analysis instruments, and applications where oil-free or chemical-resistant vacuum is required.
3. Scroll Vacuum Pumps:
- Description: Scroll pumps have two spiral-shaped scrolls—one fixed and one orbiting—which create a series of moving crescent-shaped gas pockets. As the scrolls move, gas is continuously trapped and compressed, resulting in a vacuum.
- Applications: Scroll vacuum pumps are suitable for applications requiring a clean and dry vacuum, such as analytical instruments, vacuum drying, and vacuum coating.
4. Piston Vacuum Pumps:
- Description: Piston pumps use reciprocating pistons to create a vacuum by compressing gas and then releasing it through valves. They can achieve high vacuum levels but may require lubrication.
- Applications: Piston vacuum pumps are used in applications requiring high vacuum levels, such as vacuum furnaces, freeze drying, and semiconductor manufacturing.
5. Turbo Molecular Vacuum Pumps:
- Description: Turbo pumps use high-speed rotating blades or impellers to create a molecular flow, continuously pumping gas molecules out of the system. They typically require a backing pump to operate.
- Applications: Turbo molecular pumps are used in high vacuum applications, such as semiconductor fabrication, research laboratories, and mass spectrometry.
6. Diffusion Vacuum Pumps:
- Description: Diffusion pumps rely on the diffusion of gas molecules and their subsequent removal by a high-speed jet of vapor. They operate at high vacuum levels and require a backing pump.
- Applications: Diffusion pumps are commonly used in applications requiring high vacuum levels, such as vacuum metallurgy, space simulation chambers, and particle accelerators.
7. Cryogenic Vacuum Pumps:
- Description: Cryogenic pumps use extremely low temperatures to condense and capture gas molecules, creating a vacuum. They rely on cryogenic fluids, such as liquid nitrogen or helium, for operation.
- Applications: Cryogenic vacuum pumps are used in ultra-high vacuum applications, such as particle physics research, material science, and fusion reactors.
These are just a few examples of the different types of vacuum pumps available. Each type has its advantages, limitations, and suitability for specific applications. The choice of vacuum pump depends on factors like required vacuum level, gas compatibility, reliability, cost, and the specific needs of the application.


editor by CX 2024-04-13
