Product Description
Please note :
We have almost 30 years experience in ptreol station market and post sale service support.
We are professional manufacturer of vapour recovery system, nozzles,flow meters, pumps for fuel dispensers, breakaways and swivels, etc.
We are factory in HangZhou, China.
Cordially welcome to visit our factory!
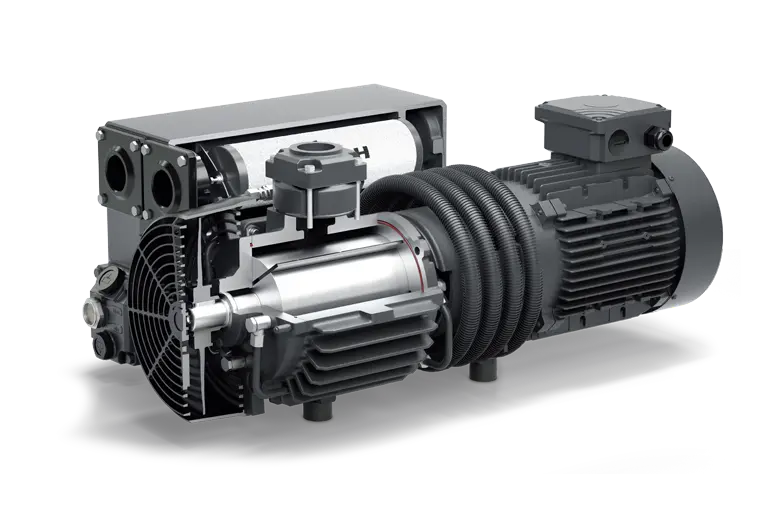
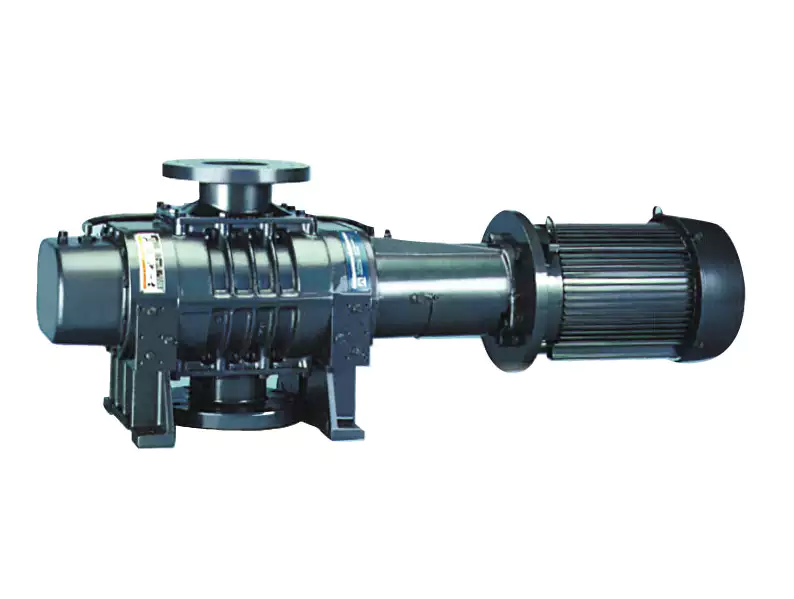
The CHINAMFG VRP-70 Vapour Recovery Pumps are vacuum pumps with integrated flame arresters arranged on the inlet and outlet sides to suck off explosion - capable fuel vapour/air mixtures into vapour recovery device s of dispensing devices at filling stations.
Features and Benefits:
Ø Protection System - To prevent a flame breakthrough in deflagrations or stable detonations of explosion - capable vapour/air mixtures of explosion group in the case of ignition on the dispensing valve and the following subsequent max. hose and pipe length: gas return hose with an internal diameter < 10mm in a coaxial hose <6mm, or optionally coaxial hose <6mm with an outer diameter <38mm, together with a subsequent ID 15pipe (G 1/2")<3mm.
Ø The gas temperature in the outlet line must not exceed 95° C±5° C.
Ø For faultless function is necessary to keep the product clean.
Ø Selective of Single pump head or double pump head.
Ø 100% Factory Tested
|
Technical Specifications |
|
|
Resistance to Pressure |
0.3 Mpa |
|
Setting Pressure |
≤0.18Mpa |
|
Max Flow rate |
70L/m |
|
Current |
<0.9A |
|
Voltage |
220V/380V |
|
Frequency |
50HZ |
|
Moter Power |
380w |
|
Motor Speed |
2820r/min |
|
Noise Sound |
<70dB |
|
Temperature |
-25° C to 55° C |
|
Net Weight |
12.80KG(Single), 14.95KG (Double) |
1- Could you develop our own design? Yes
2- The fuel nozzle including swivel? Yes
3- Can we visit your factory? Yes
4- Could you send the sample for testing? Yes
5- Could you offer door to door service? Yes
| After-sales Service: | 1 Year |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 1 Year |
| Condition: | New |
| Max Flow Rate: | 70L/M |
| Setting Pressure: | ≤0.18MPa |
| Resistance to Pressure: | 0.3MPa |
| Samples: |
US$ 275/piece
1 piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
Can Vacuum Pumps Be Used in the Aerospace Sector?
Vacuum pumps indeed have various applications in the aerospace sector. Here's a detailed explanation:
Vacuum pumps play a crucial role in several areas of the aerospace industry, supporting various processes and systems. Some of the key applications of vacuum pumps in the aerospace sector include:
1. Space Simulation Chambers: Vacuum pumps are used in space simulation chambers to replicate the low-pressure conditions experienced in outer space. These chambers are utilized for testing and validating the performance and functionality of aerospace components and systems under simulated space conditions. Vacuum pumps create and maintain the necessary vacuum environment within these chambers, allowing engineers and scientists to evaluate the behavior and response of aerospace equipment in space-like conditions.
2. Propellant Management: In space propulsion systems, vacuum pumps are employed for propellant management. They help in the transfer, circulation, and pressurization of propellants, such as liquid rocket fuels or cryogenic fluids, in both launch vehicles and spacecraft. Vacuum pumps assist in creating the required pressure differentials for propellant flow and control, ensuring efficient and reliable operation of propulsion systems.
3. Environmental Control Systems: Vacuum pumps are utilized in the environmental control systems of aircraft and spacecraft. These systems are responsible for maintaining the desired atmospheric conditions, including temperature, humidity, and cabin pressure, to ensure the comfort, safety, and well-being of crew members and passengers. Vacuum pumps are used to regulate and control the cabin pressure, facilitating the circulation of fresh air and maintaining the desired air quality within the aircraft or spacecraft.
4. Satellite Technology: Vacuum pumps find numerous applications in satellite technology. They are used in the fabrication and testing of satellite components, such as sensors, detectors, and electronic devices. Vacuum pumps help create the necessary vacuum conditions for thin film deposition, surface treatment, and testing processes, ensuring the performance and reliability of satellite equipment. Additionally, vacuum pumps are employed in satellite propulsion systems to manage propellants and provide thrust for orbital maneuvers.
5. Avionics and Instrumentation: Vacuum pumps are involved in the production and testing of avionics and instrumentation systems used in aerospace applications. They facilitate processes such as thin film deposition, vacuum encapsulation, and vacuum drying, ensuring the integrity and functionality of electronic components and circuitry. Vacuum pumps are also utilized in vacuum leak testing, where they help create a vacuum environment to detect and locate any leaks in aerospace systems and components.
6. High Altitude Testing: Vacuum pumps are used in high altitude testing facilities to simulate the low-pressure conditions encountered at high altitudes. These testing facilities are employed for evaluating the performance and functionality of aerospace equipment, such as engines, materials, and structures, under simulated high altitude conditions. Vacuum pumps create and control the required low-pressure environment, allowing engineers and researchers to assess the behavior and response of aerospace systems in high altitude scenarios.
7. Rocket Engine Testing: Vacuum pumps are crucial in rocket engine testing facilities. They are utilized to evacuate and maintain the vacuum conditions in engine test chambers or nozzles during rocket engine testing. By creating a vacuum environment, these pumps simulate the conditions experienced by rocket engines in the vacuum of space, enabling accurate testing and evaluation of engine performance, thrust levels, and efficiency.
It's important to note that aerospace applications often require specialized vacuum pumps capable of meeting stringent requirements, such as high reliability, low outgassing, compatibility with propellants or cryogenic fluids, and resistance to extreme temperatures and pressures.
In summary, vacuum pumps are extensively used in the aerospace sector for a wide range of applications, including space simulation chambers, propellant management, environmental control systems, satellite technology, avionics and instrumentation, high altitude testing, and rocket engine testing. They contribute to the development, testing, and operation of aerospace equipment, ensuring optimal performance, reliability, and safety.

What Is the Difference Between Dry and Wet Vacuum Pumps?
Dry and wet vacuum pumps are two distinct types of pumps that differ in their operating principles and applications. Here's a detailed explanation of the differences between them:
Dry Vacuum Pumps:
Dry vacuum pumps operate without the use of any lubricating fluid or sealing water in the pumping chamber. They rely on non-contact mechanisms to create a vacuum. Some common types of dry vacuum pumps include:
1. Rotary Vane Pumps: Rotary vane pumps consist of a rotor with vanes that slide in and out of slots in the rotor. The rotation of the rotor creates chambers that expand and contract, allowing the gas to be pumped. The vanes and the housing are designed to create a seal, preventing gas from flowing back into the pump. Rotary vane pumps are commonly used in laboratories, medical applications, and industrial processes where a medium vacuum level is required.
2. Dry Screw Pumps: Dry screw pumps use two or more intermeshing screws to compress and transport gas. As the screws rotate, the gas is trapped between the threads and transported from the suction side to the discharge side. Dry screw pumps are known for their high pumping speeds, low noise levels, and ability to handle various gases. They are used in applications such as semiconductor manufacturing, chemical processing, and vacuum distillation.
3. Claw Pumps: Claw pumps use two rotors with claw-shaped lobes that rotate in opposite directions. The rotation creates a series of expanding and contracting chambers, enabling gas capture and pumping. Claw pumps are known for their oil-free operation, high pumping speeds, and suitability for handling dry and clean gases. They are commonly used in applications such as automotive manufacturing, food packaging, and environmental technology.
Wet Vacuum Pumps:
Wet vacuum pumps, also known as liquid ring pumps, operate by using a liquid, typically water, to create a seal and generate a vacuum. The liquid ring serves as both the sealing medium and the working fluid. Wet vacuum pumps are commonly used in applications where a higher level of vacuum is required or when handling corrosive gases. Some key features of wet vacuum pumps include:
1. Liquid Ring Pumps: Liquid ring pumps feature an impeller with blades that rotate eccentrically within a cylindrical casing. As the impeller rotates, the liquid forms a ring against the casing due to centrifugal force. The liquid ring creates a seal, and as the impeller spins, the volume of the gas chamber decreases, leading to the compression and discharge of gas. Liquid ring pumps are known for their ability to handle wet and corrosive gases, making them suitable for applications such as chemical processing, oil refining, and wastewater treatment.
2. Water Jet Pumps: Water jet pumps utilize a jet of high-velocity water to create a vacuum. The water jet entrains gases, and the mixture is then separated in a venturi section, where the water is recirculated, and the gases are discharged. Water jet pumps are commonly used in laboratories and applications where a moderate vacuum level is required.
The main differences between dry and wet vacuum pumps can be summarized as follows:
1. Operating Principle: Dry vacuum pumps operate without the need for any sealing fluid, while wet vacuum pumps utilize a liquid ring or water as a sealing and working medium.
2. Lubrication: Dry vacuum pumps do not require lubrication since there is no contact between moving parts, whereas wet vacuum pumps require the presence of a liquid for sealing and lubrication.
3. Applications: Dry vacuum pumps are suitable for applications where a medium vacuum level is required, and oil-free operation is desired. They are commonly used in laboratories, medical settings, and various industrial processes. Wet vacuum pumps, on the other hand, are used when a higher vacuum level is needed or when handling corrosive gases. They find applications in chemical processing, oil refining, and wastewater treatment, among others.
It's important to note that the selection of a vacuum pump depends on specific requirements such as desired vacuum level, gas compatibility, operating conditions, and the nature of the application.
In summary, the primary distinction between dry and wet vacuum pumps lies in their operating principles, lubrication requirements, and applications. Dry vacuum pumps operate without any lubricating fluid, while wet vacuum pumps rely on a liquid ring or water for sealing and lubrication. The choice between dry and wet vacuum pumps depends on the specific needs of the application and the desired vacuum level.

What Are the Primary Applications of Vacuum Pumps?
Vacuum pumps have a wide range of applications across various industries. Here's a detailed explanation:
1. Industrial Processes:
Vacuum pumps play a vital role in numerous industrial processes, including:
- Vacuum Distillation: Vacuum pumps are used in distillation processes to lower the boiling points of substances, enabling separation and purification of various chemicals and compounds.
- Vacuum Drying: Vacuum pumps aid in drying processes by creating a low-pressure environment, which accelerates moisture removal from materials without excessive heat.
- Vacuum Packaging: Vacuum pumps are used in the food industry to remove air from packaging containers, prolonging the shelf life of perishable goods by reducing oxygen exposure.
- Vacuum Filtration: Filtration processes can benefit from vacuum pumps to enhance filtration rates by applying suction, facilitating faster separation of solids and liquids.
2. Laboratory and Research:
Vacuum pumps are extensively used in laboratories and research facilities for various applications:
- Vacuum Chambers: Vacuum pumps create controlled low-pressure environments within chambers for conducting experiments, testing materials, or simulating specific conditions.
- Mass Spectrometry: Mass spectrometers often utilize vacuum pumps to create the necessary vacuum conditions for ionization and analysis of samples.
- Freeze Drying: Vacuum pumps enable freeze-drying processes, where samples are frozen and then subjected to a vacuum, allowing the frozen water to sublimate directly from solid to vapor state.
- Electron Microscopy: Vacuum pumps are essential for electron microscopy techniques, providing the necessary vacuum environment for high-resolution imaging of samples.
3. Semiconductor and Electronics Industries:
High vacuum pumps are critical in the semiconductor and electronics industries for manufacturing and testing processes:
- Semiconductor Fabrication: Vacuum pumps are used in various stages of chip manufacturing, including deposition, etching, and ion implantation processes.
- Thin Film Deposition: Vacuum pumps create the required vacuum conditions for depositing thin films of materials onto substrates, as done in the production of solar panels, optical coatings, and electronic components.
- Leak Detection: Vacuum pumps are utilized in leak testing applications to detect and locate leaks in electronic components, systems, or pipelines.
4. Medical and Healthcare:
Vacuum pumps have several applications in the medical and healthcare sectors:
- Vacuum Assisted Wound Closure: Vacuum pumps are used in negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT), where they create a controlled vacuum environment to promote wound healing and removal of excess fluids.
- Laboratory Equipment: Vacuum pumps are essential in medical and scientific equipment such as vacuum ovens, freeze dryers, and centrifugal concentrators.
- Anesthesia and Medical Suction: Vacuum pumps are utilized in anesthesia machines and medical suction devices to create suction and remove fluids or gases from the patient's body.
5. HVAC and Refrigeration:
Vacuum pumps are employed in the HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) and refrigeration industries:
- Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Systems: Vacuum pumps are used during system installation, maintenance, and repair to evacuate moisture and air from refrigeration and air conditioning systems, ensuring efficient operation.
- Vacuum Insulation Panels: Vacuum pumps are utilized in the manufacturing of vacuum insulation panels, which offer superior insulation properties for buildings and appliances.
6. Power Generation:
Vacuum pumps play a role in power generation applications:
- Steam Condenser Systems: Vacuum pumps are used in power plants to remove non-condensable gases from steam condenser systems, improving thermal efficiency.
- Gas Capture: Vacuum pumps are utilized to capture and remove gases, such as hydrogen or helium, in nuclear power plants, research reactors, or particle accelerators.
These are just a few examples of the primary applications of vacuum pumps. The versatility and wide range of vacuum pump types make them essential in numerous industries, contributing to various manufacturing processes, research endeavors, and technological advancements.


editor by CX 2023-11-25
